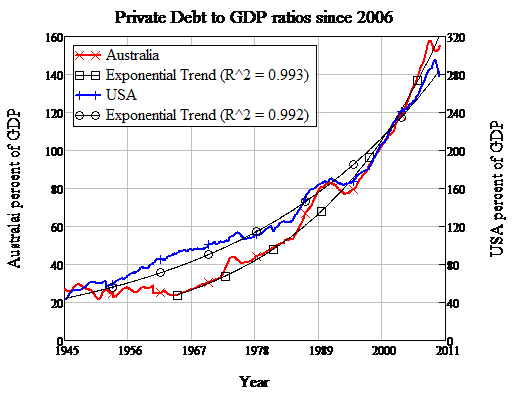
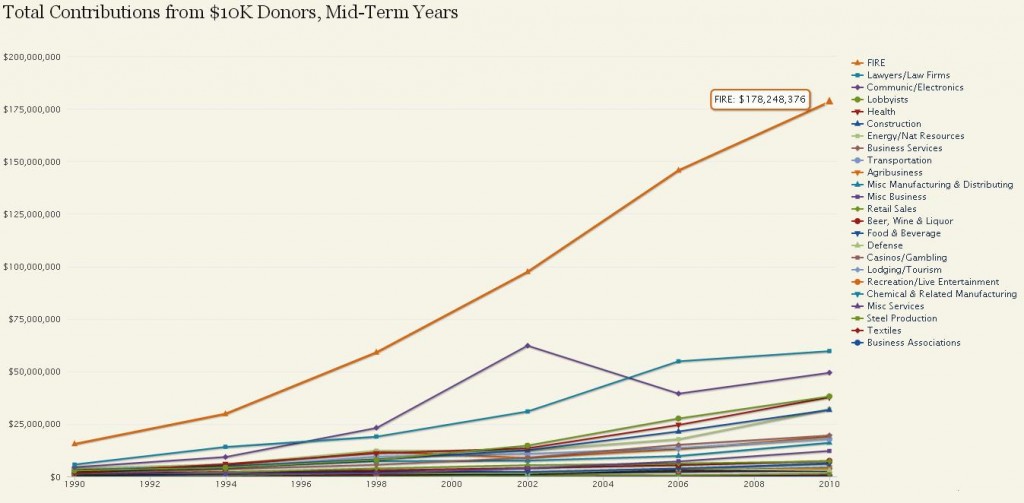
As the crisis of 2007 demonstrated, the banking system in its current form does not optimally serve the public interest. To make the system work in the best interest of the nation as a whole, I would make the following changes:
Banks
- Banks that are allowed to grant loans that create deposits would operate under the Mosler/Mitchell/Wilson proposals including:
- Be allowed direct access to government funds (details below)
- All bank levies, liquidity ratios, and reserve requirements would be eliminated.
- Banks must operate on a single balance sheet, and with no subsidiaries of any kind.
- Banks should not be allowed to engage in profit making ventures beyond basic lending; banks should profit through high quality credit analysis.
- Banks would be allowed to lend only directly to borrowers, and only for capital development purposes (i.e. business credit lines and household loans)
- Loans must be kept on their books until cleared.
- Banks cannot accept collateral.
- Banks cannot buy (or sell) credit default insurance.
- There would be a narrow banking option.
Treasury & Federal Reserve
All Federal Reserve functions would be absorbed by the Treasury. No public purpose is served by the Federal Reserve that cannot not be more democratically, efficiently, and transparently carried out by the Treasury.
Converting U.S. Government securities into federal reserves via open market operations serves no public purpose. The Treasury would fund the monetary system and public expenditure by spending zero interest perpetual bonds directly into the economy (electronically in the same manner currently used for transferring demand deposits and federal reserve accounts).
The same effect as above could be achieved by having the Federal Reserve keep the discount rate and fed funds rate target at zero and allow zero rate overdrafts by the Treasury on its deposit account. However, maintaining and allowing a Federal Reserve/Primary Dealer(s) middleman to do this serves no public purpose.
Having the Treasury spend zero interest perpetual bonds directly into the economy allows for funding full resource utilization (including mobilization/training for all idle labor). The public purpose is hindered by obfuscation from complex and needless Open Market/Primary Dealer operations. The national government maintains productivity and stable price levels through fiscal spending and taxation respectively and this should be done both directly and openly.
The fundamental structure/goals of the current FOMC will be maintained within the Treasury, with a primary mandate to maintain full productivity and a stable price level. As now, appointments to the body will outlast/overlap political and administrative terms of office, allowing the price stability mandate to remain apolitical in the manner of the current FOMC.
The role of banks and credit
The role of banks is to provide for a payments system and to fund loans based on credit analysis.
The payments system will be an open clearing system created by the state available to all on an open license. The public purpose is best served by a single public payment system.
A primary area of concern with a non-endogenous monetary system based on treasuries is that if banks are only allowed to loan funds they actually possess (in the way building societies/credit unions traditionally functioned) lending will not be sufficiently responsive to the needs of the economy. Credit is thought to be overly restricted and bank balance sheet expansion/contraction not able to nimbly adapt to prevailing economic conditions.
Crucially, the above concern over restricted credit demonstrates a failure to follow through with the full implications of a direct treasury funded system. Zero interest perpetual bonds, unlike current bank credit, will not be extinguished by loans being repaid. This is not trivial. Under this system the incentives and availability of funds for building society/S& L/credit union type institutions is vastly greater than the current system due to the way in which repayment does not extinguish money in the way it does in the current system.
The current system relies on distracting Federal Reserve/ Primary Dealer operations that maintains the destructive public belief in the “household analogy.” This is also perpetuated by the demand deposit money system. Neither of these processes serve the public and are easily bypassed.
“Endogenous” bank balance sheet expansion
In addition to building society/credit union type institutions, special banks will be allowed to grant loans that create treasury deposits, with the loaned treasuries extinguished on repayment.
These public/private partnerships are licensed to create and extinguish (as loans are repaid) zero interest perpetual Treasury bonds. They serve as intermediaries between the Treasury and businesses/individuals who are willing to take on what is in effect a special tax burden for a special privilege (treasury funding).
This process is the same as the current private endogenous demand deposit creation process which is able to nimbly expand and contract to meet changing economic conditions. However, crucially, it beneficially keeps the process on one national balance sheet. The creation of private demand-deposit money serves no public purpose that cannot be duplicated with direct-issued treasury money.
These transactions are carried out in the same way as bank credit money is created now, with the asset restrictions outlined in the “banks” section above (the Mosler/Mitchell/Wilson rules).
These special funding/taxation agreements are one more policy choice for spending into the economy, along with fiscal, tax reduction, and citizen dividend options. Crucially, the amount of spending via this channel can, unlike the current system, be easily made highly countercyclical via changes to capital requirements, loan quality assessment, and interest rates and is a policy decision like any other.
Summary: Stability, Equity, Innovation
A monetary system is made by creating and expanding a balance sheet and the public operating within the asset side of it.
Taxes (or the bank equivalent, loans) represent a debt. This debt obligation is traded around as currency. This is why taxes (or bank debt repayment) give value to a currency.
- It can be national, with government spending creating deposits and taxes destroying deposits. That is, the public swaps the government’s deposits (treasuries) around as money.
- It can be endogenous, with bank loans creating deposits and repayment destroying deposits. The public swaps banks’ demand deposits around as money.
- In the latter case when businesses/individuals choose to take out a loan beyond what the building society/credit union/mutual funds banks might provide, they in effect choose to take on greater spending and in return take on an additional tax burden (thus helping to maintain the value of the currency; taxes give value to a currency). For the good of the public and for innovation, individuals voluntarily asume a possible gain and asume a liability.
- Both systems can exist at same time with same denomination, as in modern economies.
- Both their combined total size and the balance between them is important…
Optimal total size and optimal balance
- Optimal level of total money creation = enough to keep the economy at full productivity, through both fiscal policy and through individuals having money created for them (loans) for spending on productive purposes.
- Optimum balance is enough national spending to create public goods that otherwise wouldn’t be done – i.e., infrastructure, education, full use of idle resources including idle labor, military, and health care.
- Additional spending into the economy for innovative, productive economic activity is by the special banks (endogenous) sector. This private borrowing/repaying allows private venture-type investment by individuals who agree to what is in effect voluntary taxation. This is also equitable because, unlike normal taxation, individuals ask for the additional opportunity (and accept voluntary “taxation” in return). If credit analysis is administered in the right way, this means goods created by individuals who are willing to take on rewards but also take on an additional tax.
- Both systems net to zero. This is crucial to emphasize in both systems, albeit for different reasons. In the government balance sheet expansion monetary system, it is important to realize that as a whole the system is debt free (assets and liabilities net to zero) as this highlights the fact that the government can expand the balance sheet as much as they want in order to bring all idle resources into productive use. Being clear on the equity, debt free nature of the national balance sheet crucially highlights the fact that the nation is not a household and is key to getting the public to realize that the government balance-sheet monetary system does not remotely function like a household.
- On the endogenous side, although the private endogenous system nets to zero the total size of its balance sheet relative to the monetary system matters. If the endogenous balance sheet expands greatly due to unproductive debt creation for the FIRE sector (as now), although it nets to zero it nevertheless unfairly allows real claims on real resources.
- The system balanced so that there is easy availability of the “endogenous” system to those who want to borrow/repay, but it is far more stable than the current system.
- One national balance sheet reflects the reality of our intertwined monetary-financial system and allows easier optimization of public spending and productive investment.
[I am traveling at the moment & this is a rough draft that needs editing – comments greatly appreciated]
~~~
March 28, 2019 UPDATE: The Intro to Economics textbook is finished! Live on Amazon here –